Kalman Filter Basics
·533 words·3 mins
SLAM
Kalman Filter Model and Understanding of P, Q, and R #
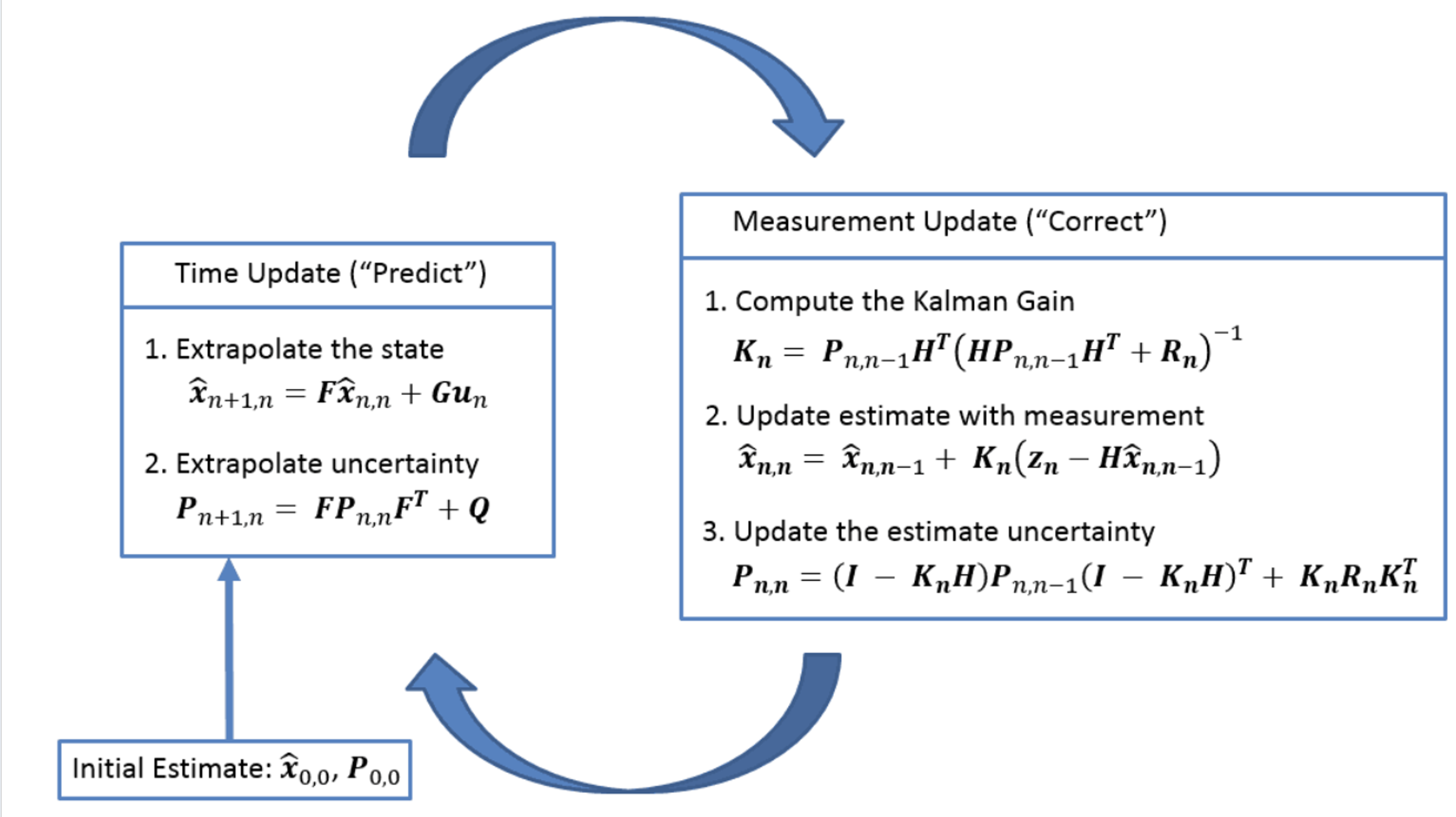
Prediction Step:
- Predicted State Estimate: $$\hat{x}{k|k-1} = F{k-1}\hat{x}{k-1|k-1} + B{k-1}u_{k-1}$$
- Predicted Covariance Estimate: $$P_{k|k-1} = F_{k-1}P_{k-1|k-1}F_{k-1}^T + Q_{k-1}$$
Update Step:
- Innovation or Measurement Residual:
$$y_k = z_k - H_k\hat{x}_{k|k-1}$$ - Innovation Covariance: $$S_k = H_kP_{k|k-1}H_k^T + R_k$$
- Kalman Gain: $$K_k = P_{k|k-1}H_k^TS_k^{-1}$$
- Updated State Estimate: $$\hat{x}{k|k} = \hat{x}{k|k-1} + K_ky_k$$
- Updated Covariance Estimate: $$P_{k|k} = (I - K_kH_k)P_{k|k-1}$$
Kalman Filter Model Components #
-
State Vector: $x$
- Represents the quantities the filter is estimating (e.g., position and velocity).
-
State Transition Matrix: $F$
- Models how the state evolves from one time step to the next.
-
Control Input Model: $B$ (if control inputs are used)
- Models how control inputs (e.g., acceleration) affect the state.
-
Control Vector: $u$
- Represents control inputs to the system.
-
Measurement Vector: $z$
- Represents the measurements used to update the state estimates.
-
Measurement Function: $H$
- Maps the state space into the measurement space.
-
Process Noise Covariance Matrix: $Q$
- Represents the uncertainty in the process model.
-
Measurement Noise Covariance Matrix: $R$
- Represents the expected noise or errors in the measurements.
-
State Covariance Matrix: $P$
- Represents the estimated accuracy of the state estimates (uncertainty in the state estimates).
Understanding of P, Q, and R #
Kalman Filter Model #
-
State Vector: $x$
- Represents the quantities the filter is estimating (e.g., position and velocity).
-
State Transition Matrix: $F$
- Models how the state evolves from one time step to the next.
-
Control Input Model: $B$ (if control inputs are used)
- Models how control inputs (e.g., acceleration) affect the state.
-
Control Vector: $u$
- Represents control inputs to the system.
-
Measurement Vector: $z$
- Represents the measurements used to update the state estimates.
-
Measurement Function: $H$
- Maps the state space into the measurement space.
-
Process Noise Covariance Matrix: $Q$
- Represents the uncertainty in the process model.
-
Measurement Noise Covariance Matrix: $R$
- Represents the expected noise or errors in the measurements.
-
State Covariance Matrix: $P$
- Represents the estimated accuracy of the state estimates (uncertainty in the state estimates).
Understanding of $P$, $Q$, and $R$ #
-
Process Noise Covariance $(Q)$
- Represents uncertainty in the process model or system dynamics.
- Larger $Q$ implies less confidence in the model, or more inherent unpredictability.
- In the prediction step, $Q$ is added to $P$ to account for the increase in uncertainty over time.
-
Measurement Noise Covariance ($R$)
- Quantifies the expected noise or errors in the sensor measurements.
- Larger $R$ indicates less reliable measurements.
- Influences the Kalman Gain $K$. Smaller $R$ increases $K$, making the filter more responsive to measurements.
-
State Covariance Matrix ($P$)
- Represents the filter’s current confidence in its state estimates.
- Updated during both prediction and correction steps.
- Smaller values in $P$ indicate higher confidence in the estimates.
Key Points #
- $Q$ adds uncertainty to $P$ in the prediction phase, acknowledging that the state becomes less certain over time without new measurements.
- $R$ affects the calculation of $K$ in the update phase. A smaller $R$ (trusting measurements more) increases $K$, leading to greater adjustment of the state estimate based on the current measurement.
- The Kalman Filter continuously adjusts the state estimate by balancing model predictions (with uncertainty $Q$) and measurement updates (with uncertainty $R$). The state covariance matrix $P$ encapsulates this balance at each step.
Related
ORB-SLAM2
·340 words·2 mins
SLAM
code reading
system setup
Linear Algebra Notes
·10 words·1 min
SLAM
Math
linear algebra notes
SLAM Basic
·36 words·1 min
SLAM
SLAM