AirDos summary
AirDos summary #
1. Introduction #
Elimination strategy can handle environments with a small number of dynamics, but cannot address challenging cases, where dynamic objects cover a large field of view as in Fig. 1(a).

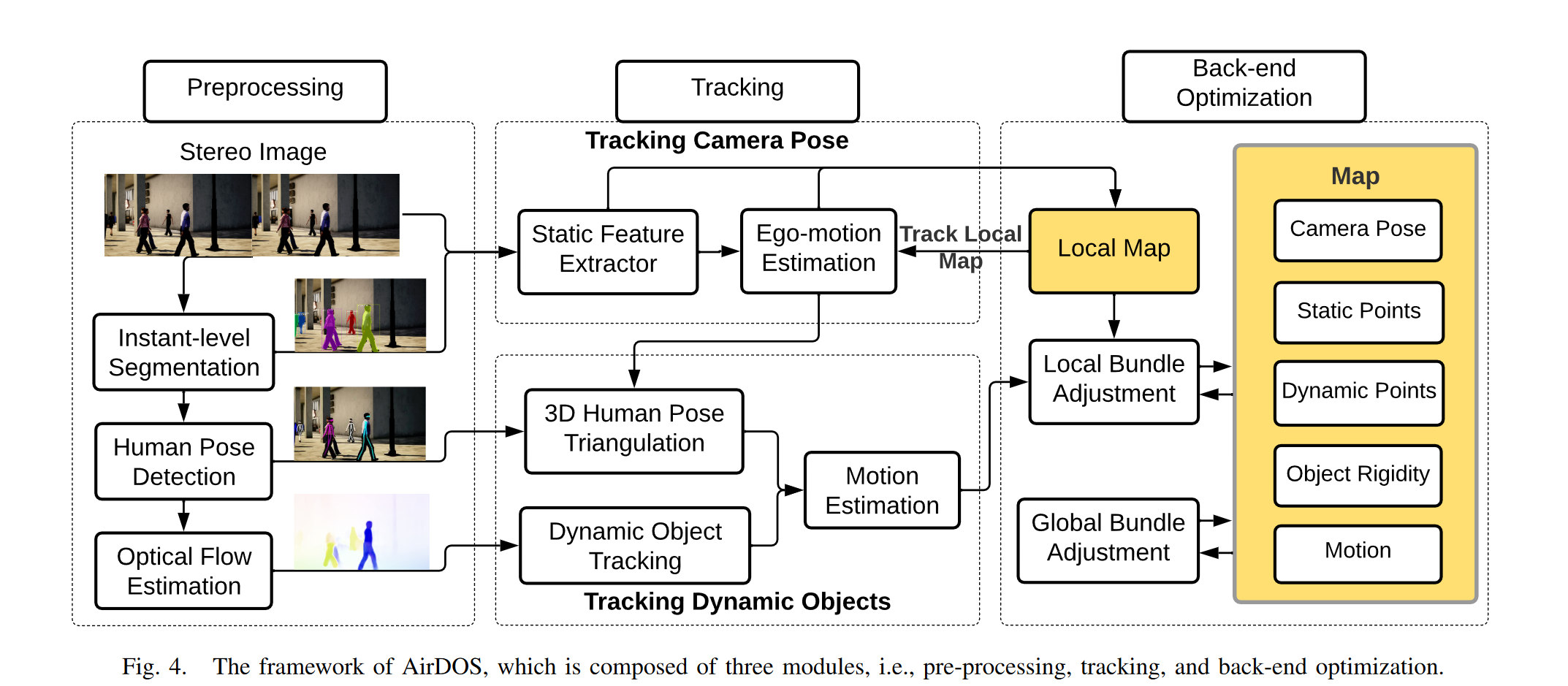
Joint Optimization Method #
- a rigidity constraint, which assumes that the distance between any two points located on the same rigid part remains constant over time.假设两点之间的距离在连续图像之间不变。
$$e_r=||_lp_k^i-{}_lp_k^j|-s^{ij}|.$$
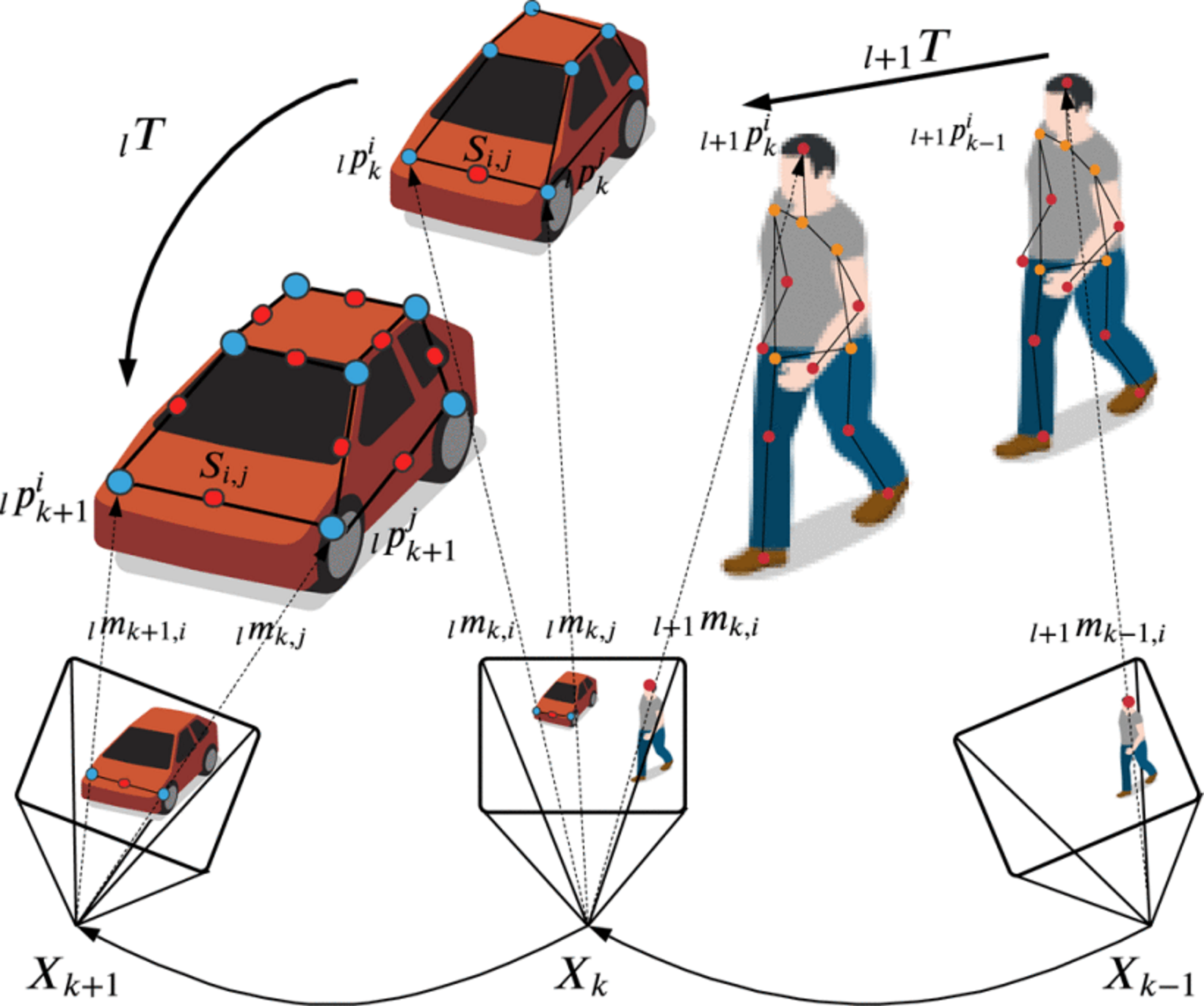
- a motion constraint, which assumes that feature points on the same rigid parts follow the same 3D motion.假设同一刚体上的特征点具有相同的运动,这里只有位移,没有旋转,所以对加法是封闭的,不用做什么处理。
$$e_m=||l\bar{p}{k+1}^i-lT{l}\bar{p}_k^i||.$$
G2O基础 #
-
顶点 (Vertex): 顶点代表优化问题中的状态变量。在g2o中,需要定义每种类型的顶点类,继承自
g2o::BaseVertex。实现setToOriginImpl()和oplusImpl()方法。 -
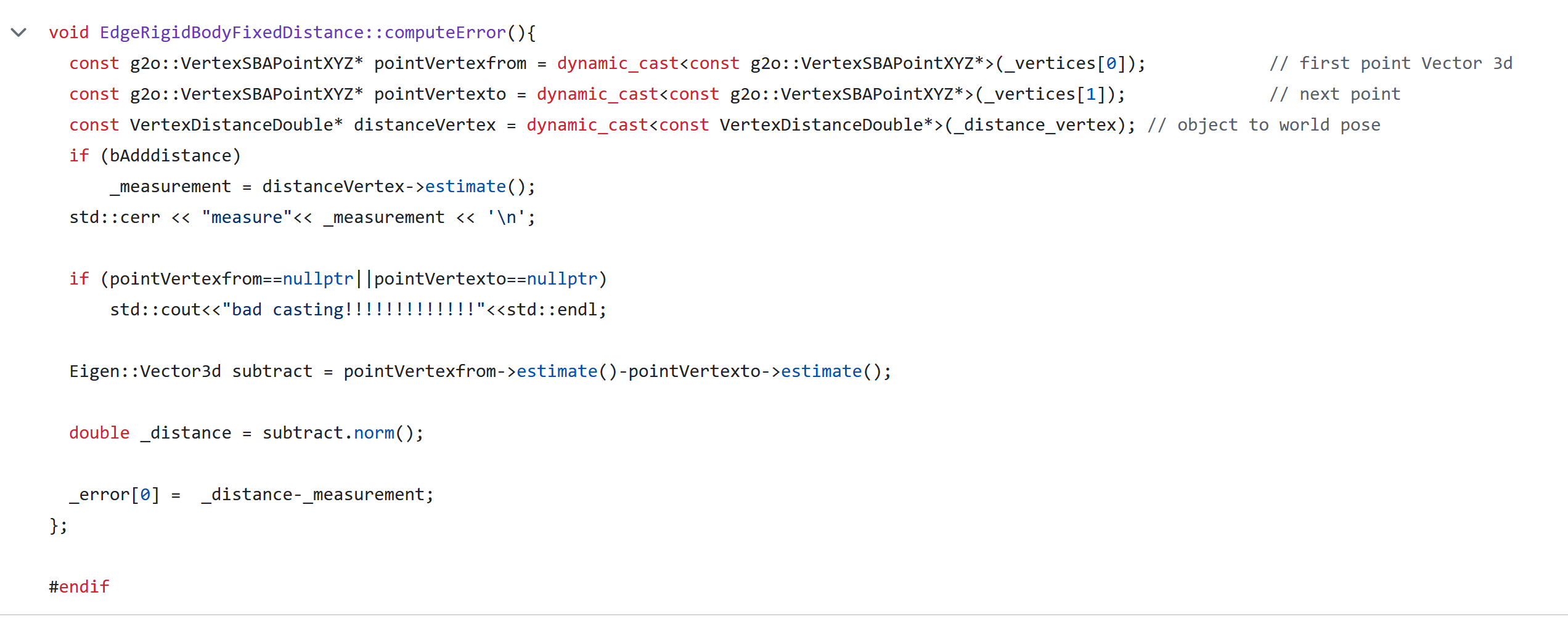
边(Edge) 边代表状态变量之间的约束或观测。在g2o中,定义边类,继承自g2o::BaseBinaryEdge或g2o::BaseUnaryEdge。实现computeError()方法。
-
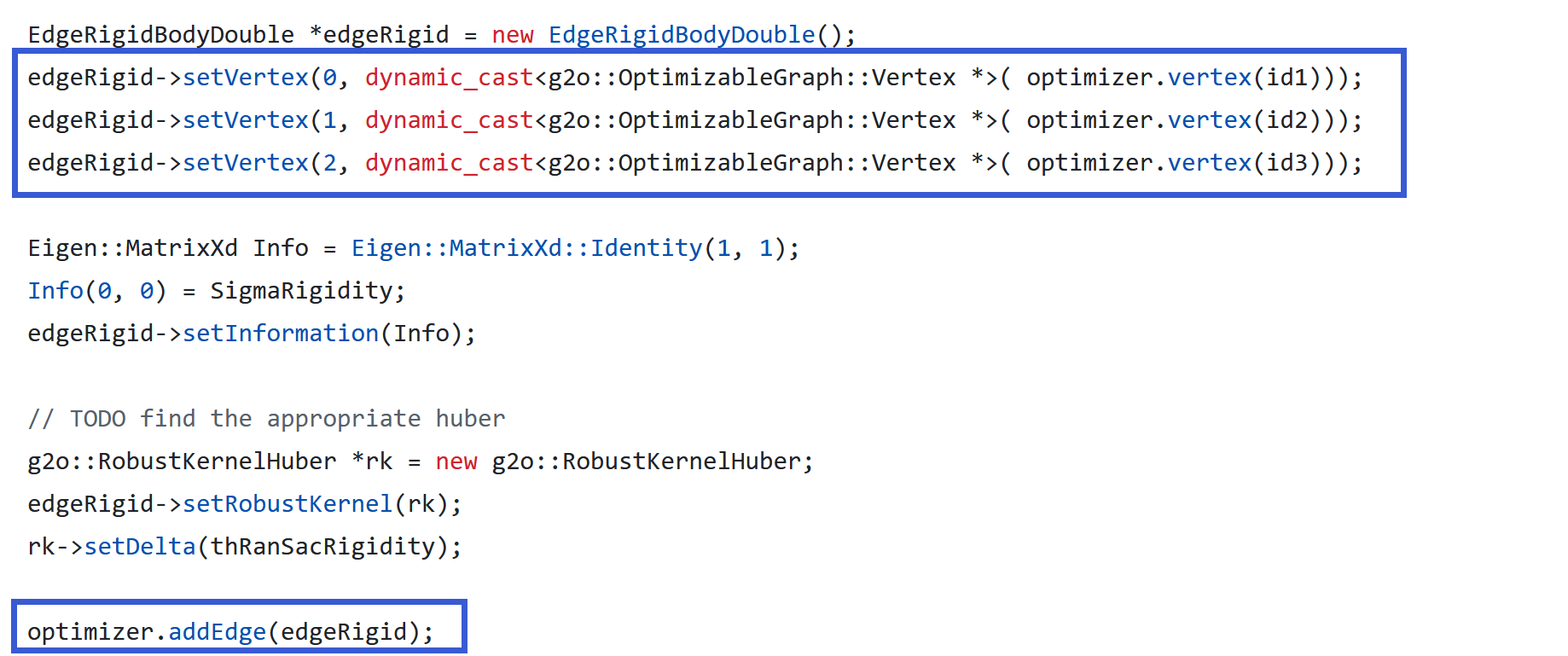
添加边和点
-
优化
